FG Neuro Psychosis
Pharmacogenetics of Psychotic Disorders
Why undergoing this examination?
The prevalence of psychotic disorders is 0.85% in the world population. Among these disorders, the most important ones are schizophrenia, bipolar psychosis, and organic psychoses. Treatment depends on the origin of psychotic disorder, as generally, antipsychotic medications, psychological therapy, and various psychosocial supports are used.
Determining factors involved in selecting an antipsychotic in an individual patient include: the primary diagnosis, psychiatric and physical comorbidities, previous treatment effects, patient preferences, treatment availability and different formulations, and above all, the expected efficacy along with drug tolerance and safety.
Despite the correct administration of antipsychotic medications, many patients do not show adequate results or experience adverse effects. The main cause is the presence of variants in the human genome, responsible for modulating the individual response to medications.
What is this exam?
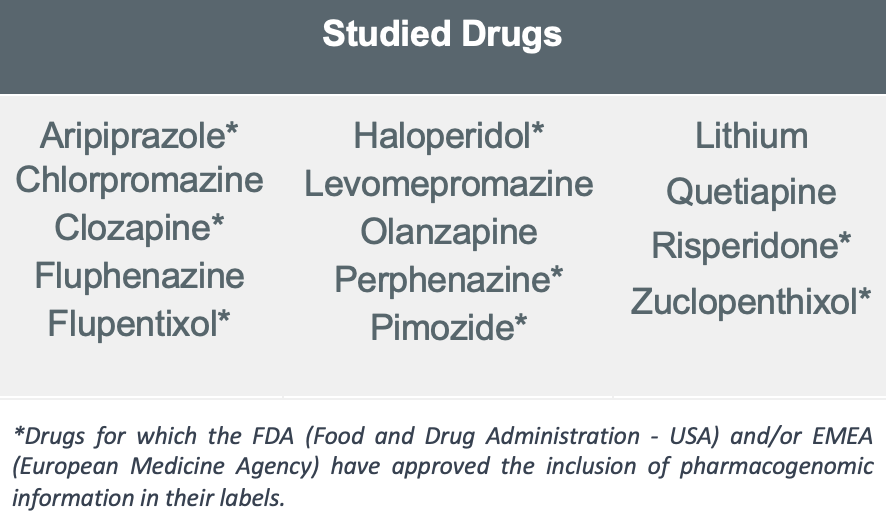
The FG Neuro Psychosis pharmacogenetic panel evaluates variants in genes responsible for the main metabolizing enzymes involved in the metabolism of antipsychotic drugs, as well as transport proteins and therapeutic targets. The analysis provides relevant information on the 14 most used drugs, based on the study of genetic variants present in the cytochrome P450 enzymes: CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP1A2, and the CACNG2 gene.
For whom is it indicated?
- Patients undergoing antipsychotic treatment who want to personalize treatment based on their genetic profile;
- Patients for whom antipsychotic treatment does not yield expected results.
Technology
Next-generation sequencing (NGS).
FG Neuro Psychosis
Pharmacogenetics of Psychotic Disorders
The prevalence of psychotic disorders is 0.85% in the world population. Among these disorders, the most important ones are schizophrenia, bipolar psychosis, and organic psychoses. Treatment depends on the origin of psychotic disorder, as generally, antipsychotic medications, psychological therapy, and various psychosocial supports are used.
Determining factors involved in selecting an antipsychotic in an individual patient include: the primary diagnosis, psychiatric and physical comorbidities, previous treatment effects, patient preferences, treatment availability and different formulations, and above all, the expected efficacy along with drug tolerance and safety.
Despite the correct administration of antipsychotic medications, many patients do not show adequate results or experience adverse effects. The main cause is the presence of variants in the human genome, responsible for modulating the individual response to medications.
The FG Neuro Psychosis pharmacogenetic panel evaluates variants in genes responsible for the main metabolizing enzymes involved in the metabolism of antipsychotic drugs, as well as transport proteins and therapeutic targets. The analysis provides relevant information on the 14 most used drugs, based on the study of genetic variants present in the cytochrome P450 enzymes: CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP1A2, and the CACNG2 gene.
- Patients undergoing antipsychotic treatment who want to personalize treatment based on their genetic profile;
- Patients for whom antipsychotic treatment does not yield expected results.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS).
Advantages
SYNLAB GROUP
Guaranteed by the experience of the absolute European leader in laboratory diagnostics.
COMPLETE
Detailed report, including the type of metabolism of each enzyme, which drugs may cause toxic effects and adverse reactions, as well as recommendations on doses.
Additional Information
DOCUMENTATION – Available on the SYNLAB Direct for clients
- Informed Consent;
- Clinical Questionnaire;
- Medical Request.
PREPARATION
- Fasting is not necessary for the test.
Additional Information

Delivery Time
22 business days
Sample Type
5mL of total blood in EDTA